| |
  |
SysMaster Security Features |
 |
 |
 |
- Layer
4 firewall module for blocking selective traffic. Traffic filters
include TCP/UDP ports, ICMP, source/destination IP addresses and
more.
- Powerful functionality for thwarting various DoS malicious attacks
based on TCP/UDP/ICMP protocols such as SYN flooding and more.
- Layer
4 IDS system for logging and alerting based on selectable type
of traffic rate thresholds. Flexible log reporting and mining.
- Easy to setup VPN module for building secure enterprise extranets.
Supports X.509 and RSA certificates. Built-in certification authority.
- Support
of Secure Network Address Translation mode of packet forwarding
when acting as a network gateway. In Secure NAT mode, well-known
ports such as 80, 443, 20, and 21 can be mapped to any port number
on the actual servers. This provides greater security by making
it difficult for intruders to identify what services are running
on which port;
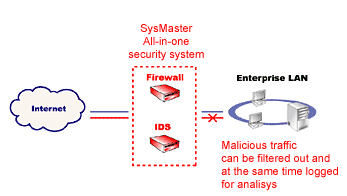
With the Firewall function module, SysMaster enhances
the security of enterprise networks. Placed at the connection point
of the network with the Internet, SysMaster filters incoming and
outgoing traffic, protecting against unauthorized access to your
computers.
The Firewall module of SysMaster acts in both incoming
and outgoing directions. Network administrators can grant Internet
access to the corporate networks only to selected "trusted" locations,
or public access can be limited to selected "safe" services. On
the other hand, outgoing traffic can also be filtered to protect
valuable data. Full Ingress/Egress packet filtering is supported
to allow dynamic packet processing, accounting, and policy data
collection and reporting.
SysMaster supports the following filtering parameters:
- IP protocol - TCP, UDP, ICMP and more;
- Source IP address;
- Destination IP address;
- Source TCP/UDP port;
- Destination TCP/UDP port;
- SYN packet filtering.
SysMaster provides alerting, logging and reporting
system for the Firewall module allowing for easy inspection of firewall
activity as well for timely warnings for suspicious traffic activity.
SysMaster is capable of filtering traffic based
on source/destination IP addresses, IP network masks, IP/TCP/UDP
ports, packet types and more. It can be configured to accept limited
traffic from specific addresses or completely prohibit all access.
In addition, specific TCP/UDP traffic, or any application based
on these protocols can be restricted. Advanced mechanism for flood
detection, such as SYN flood, PING flood and others, allows for
quick isolation of malicious attacks. SysMaster is designed to protect
itself from attacks and provide protection for the servers being
loadbalanced.
Platform Basic Security
- Basic IP spoofing prevention - prevents the IP
spoofing of the SysMaster device
- Ping-of-Death Attack
- Broadcast Amplification
- Chargen Attack
- Echo Attack
- Finger Attack
- Basic SYN Flood (local)
- Basic UDP Flood (local)
- Teardrop Attack (local)
- Land Attack (local)
Firewall Function Module
- IP Spoofing Prevention - prevents IP spoofing
for managed devices
- Smurf Attack
- Fraggle Attack
- Teardrop Attack
- Land Attack
- Efficient wire-speed Layer 4 packet processing.
- Threshold based IDS to allow capturing of legitimate traffic
only.
- Support for Logging and Alert thresholds.
- Allows setting up of IDS traps.
- Comprehensive log reporting and packet capture.
- Able to operate over high-speed networks without the dropping
of packets.
- The ability to replay stored attacks for post-mortem and forensic
analysis.
- Strong reporting capabilities.
- Manageable countermeasures.
- Easy to use Graphical User Interface.
- Secure remote administration capability.
- Archival facilities.
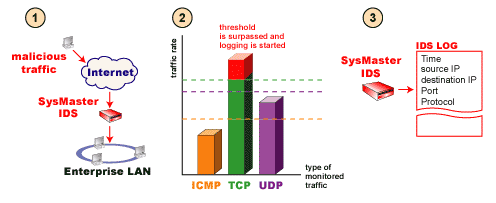
- SysMaster IDS monitors incoming and outgoing traffic.
- SysMaster IDS detects a TCP traffic with rate exceeding
the threshold set for this type of traffic.
- SysMaster IDS starts recording the traffic into its log and/or
sends email alerts to system administrators alerting them for
the breach.
L4 IDS allows high performance and efficiency for
packet processing at wire speed. Intrusion detection is initiated
once defined packet/byte thresholds are exceeded. Once the thresholds
are exceeded packet logging and alert is initiated. The packets
can then be investigated via a comprehensive reporting feature to
identify hostile IP addresses.
SysMaster detects, protects and reports about the
following type of attacks:
- SYN
Flood
When one computer system wants to establish a connection with
another, a process is used called a three-way-handshake. The source
sends a packet of data (a SYN) to the destination, the destination
acknowledges and replies (SYN ack) to the source and waits for
the source address to send a final acknowledgment (another ack).
Attackers have used this to send bogus SYN packets containing
spoofed source IP addresses to targeted web servers. This means
that the destination server waits for a response that is not going
to happen. When this is done multiple times from multiple sources
it floods the destination server, which has a limit of unacknowledged
SYN's or responses it can handle. This will ultimately bring down
the server.
- Page
Flood
A page flood is when one or web pages are requested enough times
to emceed the servers capacity to download the data.
- Smurf
Attack
A Smurf attack floods your router with Internet
Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets (pings).
The destination address of each packet is the broadcast address
of your network therefore creating a large amount of ICMP echo
request and response traffic. Some Smurf attacks spoof the source
IP address compounding the problem.
- Fraggle
Attack
A Fraggle attack uses UDP packets to unwittingly
use ICMP echo requests in the same way as a Smurf attack.
- UDP
Attack
UDP floods happen when many packets of data are
sent via UDP with a spoofed source address. This results in a
backlog of UDP responses.
- ICMP
Flood Attack
A victim is sent a huge stream of ICMP packets.
There are so many that the server cannot handle them exhausting
bandwidth and hanging the server.
- Ping
of Death
Certain systems will crash if they receive an ICMP
packet that has been maliciously corrupted.
- Teardrop
This attack relies on system vulnerability that
causes many systems to crash when they receive IP packets that
have been corrupted so that the data overlaps.
- Land
Certain systems will exhaust their resources when
they receive a packet with the same source and destination address.
- Chargen
Certain systems will crash when they try and process
a packet with the same source and destination address, similar
to a Smurf attack.
Layer 7 IDS
SysMaster implements OSI Layer 7 IDS protection
covering protocols such as DNS, SMTP, HTTP and more.
- DNS attack reporting
DNS poisoning replaces the name of a victim system with another
system's name by either corrupting the name service cache of the
victim system, or by compromising a domain name server for a valid
domain. The DNS Cache poisoning attack affects all versions of
BIND, and Windows DNS server. SysMaster reports all suspicious
traffic either as an email/pager alert or to its log system.
- SMTP virus reporting
SysMaster analyses all traffic that passes in and out of the protected
network. It can detect any specific signature that relates to
malicious attack such as viruses distributed via emails. The IDS
module logs also reconnaissance attacks trying to retrieve information
about user names.
- HTTP reporting
SysMaster can report about any suspicious traffic that passes
in and out of the network using the HTTP protocol including viruses.
SysMaster can track known attempts for malicious breaking into
web servers. This is done by inspecting the HTTP headers (containing
calls to CGIs) using keyword matching.
|
|